On this page important questions about horse hair analysis are clarified. The answers should help to better understand what a hair analysis is all about and how great the benefits can be.
What is the difference between hair analysis and hair mineral analysis?
What is the difference between an analysis for sport/competition horses and an analysis for leisure horses?
Why should a hair analysis be performed?
Which hairs should be used for a hair sample?
How long should the hair be for a hair analysis?
Are known diseases or special features of the animal to be disclosed?
Does hair have to be prepared for the hair sample?
Which device is best suited for the hair analysis?
How reliable is a horse hair analysis?
Where are hair analyses used?
What are the main benefits of a horse hair analysis?
At what intervals should a horse hair analysis be performed?
What effects do care products have on the horse hair or analysis?
Can hair be unsuitable for a horse hair analysis?
How can a therapeutic success be measured?
Can a hair analysis be used as a precaution?
Why can a hair analysis be used for a long time?
How long does a horse hair analysis take?
Who are the customers?
What is special about your work?
What is the difference between hair analysis and hair mineral analysis?
Again and again the term hair mineral analysis is used in connection with hair analyses. This must not be confused. Of course, if desired, only an analysis of vitamins, minerals and trace elements can be performed. The question arises as to the purpose of a client for a hair analysis. Mineral analysis is mostly done by laboratories. The comparison is obvious:
A hair mineral analysis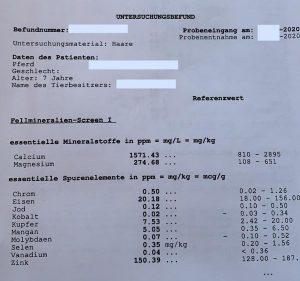
(click to enlarge)
or a full horse hair analysis (click)
If in doubt, feel free to call and ask for more information.
What is the difference between an analysis for sport/competition horses and an analysis for leisure horses?
In the case of competition horses, a small performance test is also carried out.
Furthermore – very important (!) – the therapy plan must be checked for doping (ADMR). Even if a horse is not currently competing, there are medications that should be given concomitantly (i.e. always), either to treat a horse or to keep a future illness at bay. In these cases, the horse owner needs to know how long a drug should be discontinued before a competition so that it does not fall under doping.
If a product falls under doping, a test is first carried out to determine whether a doping-free product can be selected.
In the case of leisure horses, the ADMR test and the search for alternative medication is not necessary.
Why should a hair analysis be performed?
In everyday life there are always situations in which it is puzzling what the animal is currently suffering from. These can be behavioral problems, fears, aggression, etc. Sometimes therapists are at the end of their rope and the cure is based on a random diagnosis. In the past, a hair analysis has almost always brought the true cause to light in such cases. The question is how long the horse should continue to be uncomfortable.
Which hairs should be used for a hair sample?
The best way to answer this question is to determine where hair is easiest to take. Depending on the condition, it could sometimes be a little more difficult to obtain coat hairs for a hair sample. Therefore it is recommended to use hairs which can be taken easily, uncomplicatedly and painlessly.
How long should the hair be for a hair analysis?
The length of the hair should be 3 to 4 cm if possible. Normally, shorter hairs (2 to 3 cm) are also suitable. Our specification is only a length for safety.
Are known diseases or special features of the animal to be disclosed?
The purpose of hair analysis is to analyze the health of the organism. The knowledge about existing diseases / ailments etc. could possibly affect the analysis result. Therefore, it is recommended not to give any information about the health condition at first.
Does hair have to be prepared for the hair sample?
There is no need to pre-treat the hair. Even if residues of oils, care products or medications adhere to the hair, this will not affect the analysis result.
Which device is best suited for the hair analysis?
There are different devices available on the market. What matters is the experience of the therapist. It is quite possible to achieve a better result with a less powerful device.
How reliable is a horse hair analysis?
The results of a hair analysis are very reliable. A horse hair is practically like a personal code. Such a code is so individual and unique that it is almost comparable to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
Where are hair analyses used?
In everyday life, there are different areas of application for hair analysis. Hair analysis is used in forensic medicine and forensics. Hair analyses are useful for the detection of drugs or alcohol. Minerals, environmental pollution (especially environmental toxins), trace elements, etc. are shown in a hair analysis.
What are the main benefits of a horse hair analysis?
The collection of the hair sample is very simple. Packaging, storage and transport are uncomplicated. The substances, which are absorbed in a hair, remain permanently.
At what intervals should a horse hair analysis be performed?
In principle, a single horse hair analysis is sufficient, because the information is permanently stored in the horse hair. In certain cases, it may be helpful to perform another analysis. This would be conceivable if a hair analysis was performed a long time ago. A new disease, which has only existed for some time, may not have manifested itself in the last hair sample.
What effects do care products have on the horse hair or analysis?
If the horse hair has been treated with care products (shampoo, oils, etc.), this has no effect on the results.
Can hair be unsuitable for a horse hair analysis?
This question can be answered with no. Neither grooming products nor other treatments of hair (braiding, waving, curling, etc.) have any effect on the results of horse hair analysis. The only criteria for the horse hair sample are hair length and number of hairs.
If a horse has a very short mane, or it is not possible to take hairs from the mane, there is a possibility to use e.g. hairs from the tail or from the coat. If these alternatives also fail, the collection of blood, urine, etc. remains. However, this should be requested in advance.
How can a therapeutic success be measured?
Basically, the success of the therapy can be determined by the physical condition of the horse. Beyond that, however, a new hair analysis can be performed after an appropriate waiting period. However, the waiting period should be approximately one year after the first or previous horse hair analysis.
Can a hair analysis be used for preventive measures?
The analysis results are designed to show how intensively an organism is affected by a disease symptom. It is always shown, for example, whether the horse is currently affected by a symptom and thus impaired. In the same way, it is shown whether the horse is susceptible to a certain disease.
It is not possible to see when or if a certain characteristic will break out at all. In this regard, appropriate precautions can be taken if necessary.
Why can a hair analysis be used for a long time?
For example, information regarding Cushing’s syndrome is stored in the horse’s hair, which currently affects the horse. In the same way, a geoapathic load (e.g. electrosmog, water veins, etc.) can be found, which does not currently affect the horse. The geoapathic stress does not necessarily have a negative effect on the organism, but according to the analysis result, the horse would be susceptible.
If at some point the horse were to be housed in a stable or stall where a water vein, for example, runs in the soil, this could lead to detrimental effects on that horse.
Without the information from the hair analysis, this option might not have even been considered. The information in each individual hair is coded similarly to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Once the information is registered in the hair, it remains stored there for all time.
How long does a horse hair analysis take?
A detailed horse hair analysis takes at least two hours. For follow-up analyses or questions about specific diseases or symptoms, the time required may be reduced to some extent.
Who are the customers?
For reasons of discretion, no names of people or horses will be mentioned. However, we are pleased to count winners of l’Arc de Triomphe (one of the most important horse races internationally), the King George VI & Queen Elizabeth Stakes – both in gallop racing – or Olympic champions as well as German champions in show jumping, dressage, eventing etc. among our valued customers.
What is special about your work?
Every horse is analyzed and treated with the same care as if it were my own horse. This is reflected in the therapy plan, among other things. Less is often more.
